Table Of Content
The most common approach to course design is to begin with a consideration of the most suitable methodologies for teaching content. In other words, the focus is typically on how the content will be taught, rather than on what is to be taught. However, Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe argue that this framework is flawed, because its emphasis on teaching methods is misplaced.

Instruction
Browse over 500+ educator courses and numerous certificates to enhance your curriculum and earn credit toward salary advancement. Please consider supporting us and gaining full access - click here to become a member.
Table of Contents
Working backwards to design a new user experience for Virtual Engineering Workbenches on AWS Amazon Web ... - AWS Blog
Working backwards to design a new user experience for Virtual Engineering Workbenches on AWS Amazon Web ....
Posted: Fri, 28 Jul 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
As the quote below highlights, teaching is not just about engaging students in content. It is also about ensuring students have the resources necessary to understand. Student learning and understanding can be gauged more accurately through a backward design approach since it leverages what students will need to know and understand during the design process in order to progress. As the quote below highlights, teaching is not just about engaging students in the content.
Instructional Design
Performance-based assessments are best suited for collecting evidence about the depth of knowledge that has been obtained. The final stage of backward design is choosing learning activities that are aligned with the learning goal and the assessment. While there are many approaches to planning a course, backward design is a useful framework that puts at the forefront what matters most—student learning. Unlike content-oriented approaches, the backward design process begins by determining learning goals and outcomes for students.
Incorporating a backward-forward stochastic particle tracking model into a hydraulic modeling framework to identify ... - ScienceDirect.com
Incorporating a backward-forward stochastic particle tracking model into a hydraulic modeling framework to identify ....
Posted: Tue, 23 Jan 2024 07:27:23 GMT [source]
However, these ILOs still communicate crucial information to students about what good communication looks like to the instructor and help them better understand what will be expected of them in the course. In the well-known book The Seven Habits of Highly Effective People, author Dr. Stephen Covey describes seven habits that successful people tend to live by. The second habit is “Begin with the end in mind.” Dr. Covey was suggesting that the most successful people are those who create a vision of the future in their mind. They determine what they want to be and do, and then take actions to reach that result.
WHY SHOULD I USE BACKWARD DESIGN IN MY COURSES?
This approach applies to any field, including business, the sciences and STEM. Assessment refers to the wide variety of methods or tools that educators use to evaluate, measure, and document the academic readiness, learning progress, skill acquisition, or educational needs of students. Bloom’s Taxonomy is a great tool in helping to identify action verbs appropriate for measurement. Use specific action verbs to express exactly the kinds of skills you want your students to develop.
That's a quick tour of how Backward Design came to be and how it's changed the world of education and training. Like any journey, knowing where you've come from can help you understand where you're going. And in the world of Backward Design, it's always about reaching meaningful destinations. To connect directly with our partners for teaching support or for help with Ohio State eLearning tools, visit our help forms. Reflect upon the impacts of climate change on their local communities and in their everyday lives. Professor Buckeye has been asked to teach an introductory course on a standard topic in his discipline—it’s a course he’s never taught before and it’s not exactly in his area of expertise.
Learner-Centered vs Content-Centered Approach
You will follow the same step-by-step process above, but there are a few additional elements to consider during Steps 3-5. I mean, even though I loved the book, my students’ response to it was mostly lukewarm. Maybe it was the connections I was able to make to the stuff students dealt with on a day-to-day basis. I taught that book a few times, and even though I looked forward to it every time, I always finished the unit a little unsatisfied. When I taught seventh grade language arts, one of my favorite things to teach was S.E. After we did some reflecting, writing, and talking, we were ready to start the book.
You then develop assignments that will help students practice and meet those outcomes. Decisions about course content and teaching strategies appear last, guided by reflection on what students will need to demonstrate their learning. As previously stated, backward design is beneficial to instructors because it innately encourages intentionality during the design process. It continually encourages the instructor to establish the purpose of doing something before implementing it into the curriculum.
According to Vygotsky, this "zone" is the gap between what learners can do independently and what they can achieve with guidance. When you set goals upfront, you may base them on assumptions about student potential. These assumptions may not accommodate the needs or potential of individual students. Research over the past several decades has shown that students learn more and retain their learning longer if they acquire it in an active rather than a passive manner. In the past, classroom instruction has focused on the instructor and the ways in which the subject matter could best be presented to the student. Examples of summative assessments include exams, portfolios, presentations, written work.
One reason so many of us don’t remember much of what we learned in school is that we learned it through this haphazard, topic-driven approach. These random activities are taking up precious time that could be spent on much more valuable stuff. This is the same philosophy that follows many standardized tests in public schools around the country. Public school teachers will often “teach the test” by focusing primarily on what will be on federal or state standardized tests instead of other content or modules in textbooks. Do you have a final exam surrounding a few modules from a book or from an online class? Make sure that the exam has a section for each module so students can study the entire course’s material from start to finish.
Backward design works best when the school or district develops its own tests so they know what the targets are. Even without the knowledge of what is on the tests, most districts tend to favor backward design or backloading because there is great pressure from the stakeholders for students to attain high test scores. In private schools, where high-stakes testing is not as much of an issue, curriculum development is most often frontloaded, particularly with classical education where the aims, goals, and objectives are of primary importance.
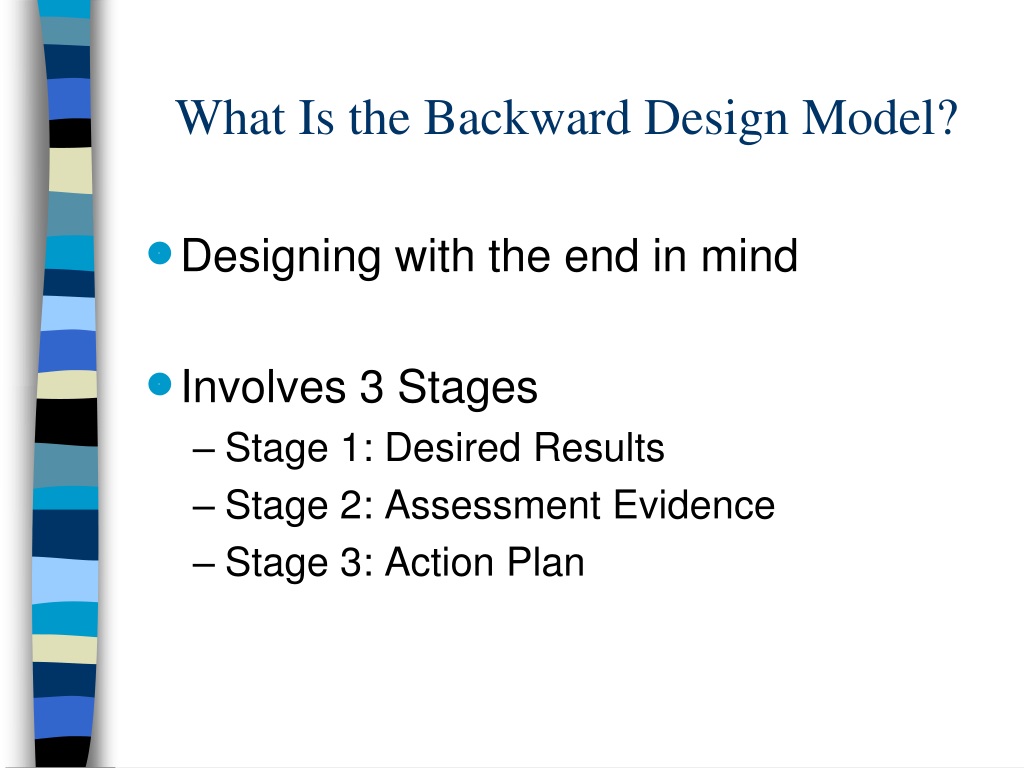
Backward Design is an instructional design approach that begins by first defining the desired outcomes and objectives and then creating the assessments, instructional activities, and materials to help learners achieve those outcomes. This approach to curriculum and lesson planning prioritizes learning objectives, resulting in more effective and purposeful teaching and more student-centered and engaging learning experiences. Backward design is a method of curriculum planning in which standards are aligned with assessments and lesson plans through the use of a 3-stage process. It was discussed in the book Understanding by Design by Grant Wiggins and Jay McTighe.
As you backward design your course, you should be planning with all students in mind. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is a framework for focusing curriculum and course design around the diverse needs of learners. Backward design and UDL are complementary frameworks for course planning, as each are centered on student learning and purposeful, proactive course design.
The idea of Backward Design comes from Wiggins & McTighe and suggests that learning experiences should be planned with the final assessment in mind. There are lots of advantages to using backward design for your lesson plans. For starters, it ensures that your students will never be flabbergasted or taken by surprise by testing materials. They will never sit for a test and not know what the test is talking about or what he wants them to do. Unfortunately, this results in tests or assessments that don’t always reflect what the students did or learned. We’ve all experienced an unfortunate class or two where the test didn’t seem to reflect anything we had learned in lessons or course materials up until that point.
No comments:
Post a Comment